Tag: generic drugs
Bioequivalence for Inhalers, Patches, and Injections: What Generic Drugs Must Prove to Work the Same
Bioequivalence for inhalers, patches, and injections isn't about matching blood levels-it's about ensuring the drug reaches the right place the same way. Learn why these generics are harder to approve, cost millions more, and still save lives.
Economic Impact of Patent Expiration: When Drug Prices Drop
When pharmaceutical patents expire, drug prices can drop by up to 82% as generics enter the market. But delays from rebates, formularies, and patent thickets often block savings. Here’s how it really works-and what you can do to save.
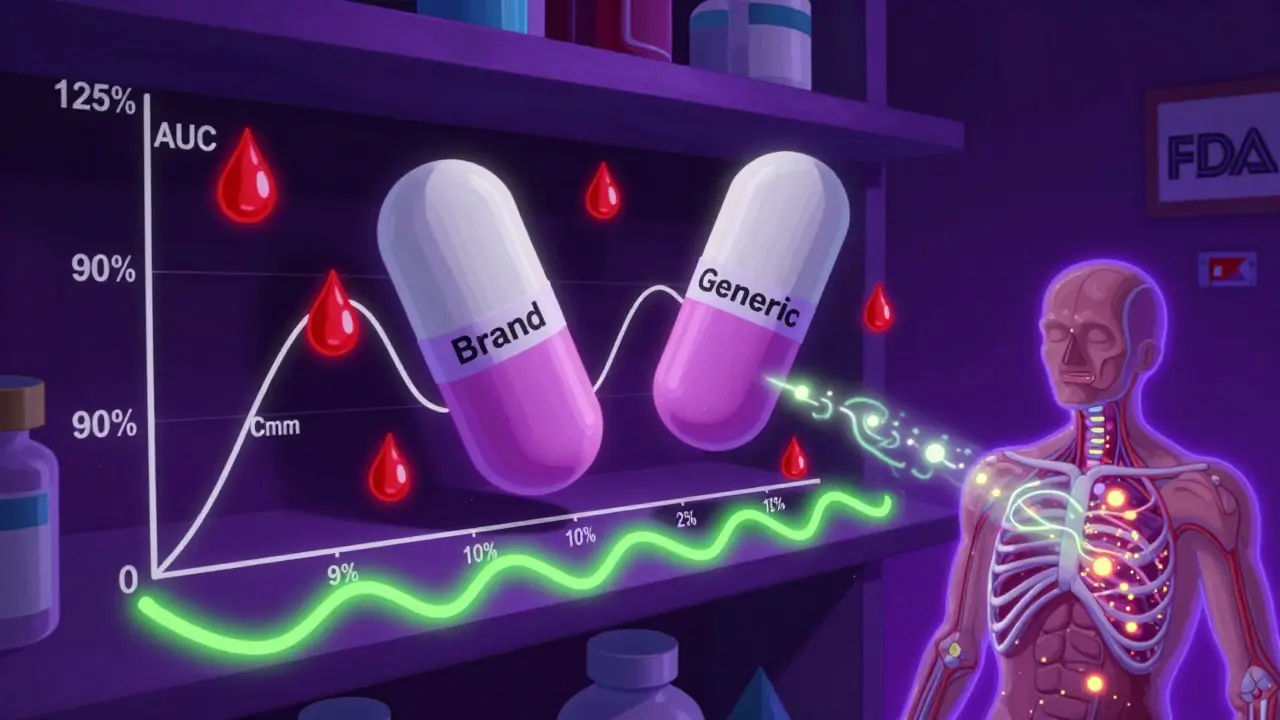
The 80-125% Rule: Understanding Bioequivalence Confidence Intervals in Generic Drugs
The 80-125% rule ensures generic drugs are as safe and effective as brand-name versions by measuring how much of the drug enters your bloodstream. It's based on statistical confidence intervals, not pill content.
Do Patients Really Choose Authorized Generics? What the Data Shows
Patients often prefer authorized generics over traditional ones because they're identical to brand-name drugs-same ingredients, same manufacturer. But price still drives most choices after the initial 180-day window. Here's what the data really shows.
Compulsory Licensing: How Governments Can Override Patents in Emergencies
Compulsory licensing lets governments override patents to make life-saving drugs affordable during emergencies. Used in HIV, COVID-19, and cancer treatments, it balances innovation with public health needs.
Medical Education on Generics: Do Doctors Learn Equivalence?
Despite generics making up 90% of prescriptions, most doctors receive little training on bioequivalence. This article explores why physicians still doubt generic drugs and what medical education must change to close the knowledge-behavior gap.
Authorized Generics vs Traditional Generics: What You Need to Know
Authorized generics are exact copies of brand-name drugs, while traditional generics may have different inactive ingredients. Learn the key differences, when each matters, and how to ensure you get the right one.
Clinical Outcomes Data: What Studies Tell Providers About Generics
Clinical outcomes data shows generic drugs are just as effective and safe as brand-name medications for most conditions. Providers can confidently prescribe generics to improve adherence and reduce costs without compromising care.